Valid Names Results
Lepidosaphes chinensis Chamberlin, 1925 (Diaspididae: Lepidosaphes)Nomenclatural History
- Lepidosaphes chinensis Chamberlin 1925a: 85-86. Type data: CHINA: Guangdon, Canton, on Magnolia sp., 1925, by F. Silvestri. Holotype, female, Type depository: San Francisco: California Academy of Sciences, Department of Entomology, California, USA; accepted valid name Notes: Paratypes in BMNH, UCDC and USNM.
- Cornuaspis chinensis (Chamberlin, 1925); Borchsenius 1963: 1168. change of combination
Common Names
- Chinese lepidosaphes scale McKenz1956
- Chinese Mussel Scale MalumpHaSa2012
Ecological Associates
Hosts:
Families: 9 | Genera: 15
- Arecaceae
- Rhapis | Suh2016
- Asparagaceae
- Beaucarnea recurvata | MalumpHaSa2012
- Dracaena braunii | MalumpHaSa2012 | (= Dracaena sanderiana)
- Liriope | Tang1986
- Rohdea | Suh2016
- Sansevieria trifasciata | MalumpHaSa2012
- Yucca gigantea | MalumpHaSa2012 | (= Yucca elephantipes)
- Elaeagnaceae
- Elaeagnus umbellata | Takaha1936a
- Euphorbiaceae
- Euphorbia elegans | MalumpHaSa2012
- Fabaceae
- Indigofera tinctoria | Tao1999
- Lamiaceae
- Caryopteris incana | Tao1999
- Magnoliaceae
- Magnolia | Chambe1925aJC
- Orchidaceae
- Cymbidium | Ferris1938a
- Cymbidium aloifolium | Takaha1936a
- Cymbidium sinense | MartinLa2011
- Schomburgkia | Nakaha1982
- Pandanaceae
- Pandanus | Hunt1939
Geographic Distribution
Countries: 6
- China
- Fujian (=Fukien) | Tang1986
- Guangdong (=Kwangtung) | Chambe1925aJC
- Guangxi (=Kwangsi) | Tang1986
- Jiangsu (=Kiangsu) | Tao1999
- Shanghai | Takaha1936a
- Xianggang (=Hong Kong) | MartinLa2011
- Philippines | Hunt1939
- Singapore | Nakaha1982
- Taiwan | Takaha1936a
- United Kingdom
- England | MalumpHaSa2012
- United States
- California | Ferris1938a
- Florida | Stocks2014a
Keys
- PowellZeMi2024: pp.19 ( Adult (F) ) [Key to slide-mounted Lepidosaphes]
- SuhJi2009: pp.1041-1043 ( Adult (F) ) [Key to species of armored scales intercepted on imported plants (slide mounted females)]
- Gill1997: pp.168 ( Adult (F) ) [Key to California species of Lepidosaphes]
- Chou1982: pp.155 ( Adult (F) ) [Key to Chinese species of Lepidosaphes]
- McKenz1956: pp.32 ( Adult (F) ) [Key to species of Lepidosaphes]
- Ferris1942: pp.SIV-446:56 ( Adult (F) ) [Key to species of Lepidosaphes]
Remarks
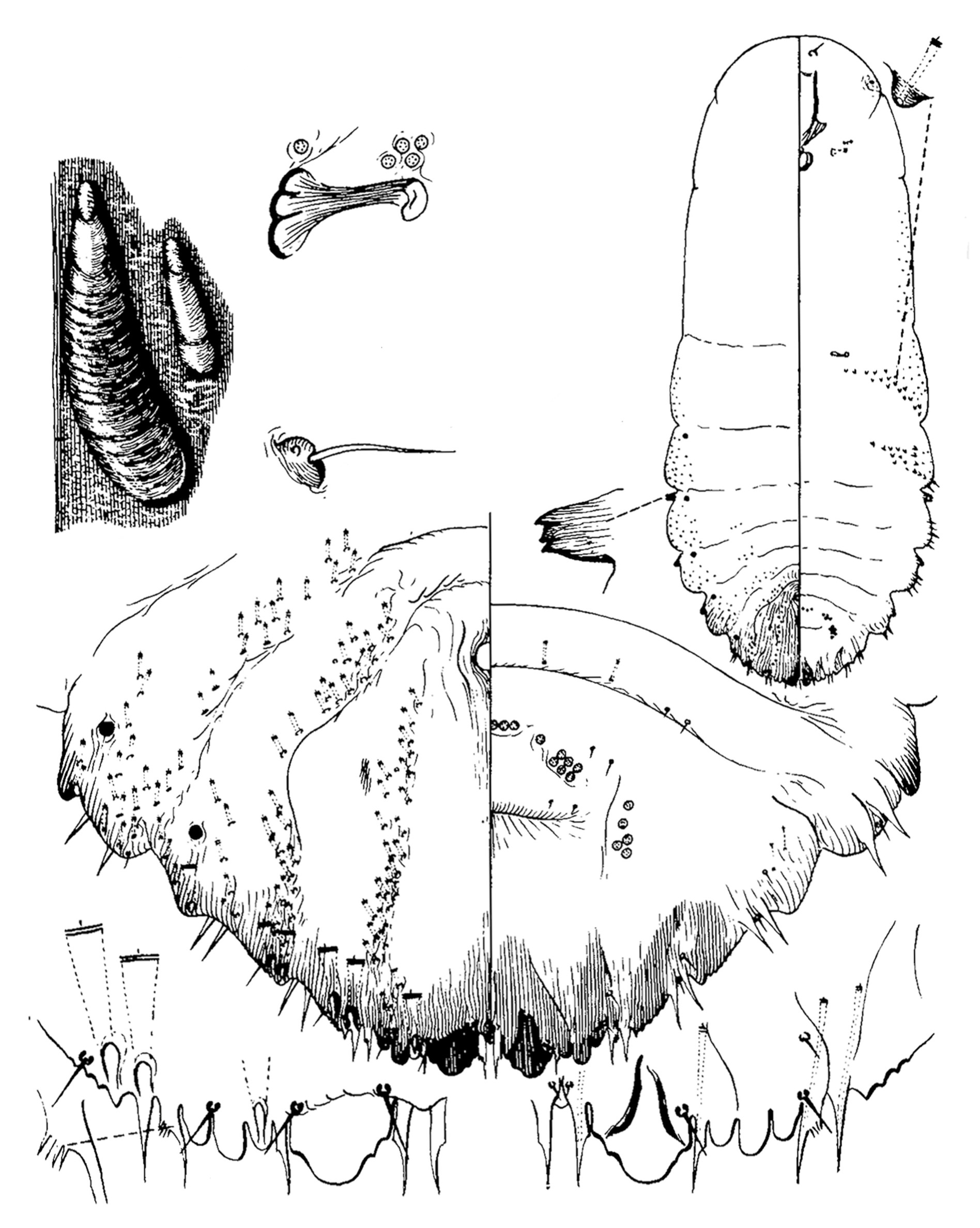
- Systematics: Lepidosaphes chinensis may most easily be confused with L. ulmi and L. beckii. It may be distinguished from the latter by the presence of marginal spurs, which are lacking in the L. beckii and by the presence of bosses on segments 1 to 5, while in L. beckii these bosses are present only on segments 1, 2 and 4 (Ferris, 1938a).
- Structure: Female scale moderately broad. Male scale quite long and slender, both are light brown. Adult female about 0.9 mm long (Ferris, 1938a). The adult female scale covers are up to 3.0 mm in length, moderately broad, slightly convex, and pale to orange brown with a dark orange terminal exuviae. Adult female bodies are white with the margin of the pygidium yellow to orange. Male scale covers are much smaller and narrower than the female covers, up to 1.5 mm in length elongate oval, slightly convex, and pale brown with a dark orange terminal exuviae. Male prepupae and pupae are pale lilac, with their eyes deep purple. First instars (crawlers) of both sexes are white and their covers are also white. Second instar scale covers are brown with a dark orange terminal exuvia. (Malumphy, et al., 2012)
- Biology: All developmental stages occur on the stems and foliage (upper and lower surfaces) of the host plant. It is sexually reproductive and each female lays between 32 and 38 eggs. All life stages (except adult males, although male pupae were present) were observed in November which suggests that it may have overlapping generations and be multivoltine if environmental conditions are favourable. There were approximately two male scale covers for every female scale, although the sex ratio varied considerably on different leaves. (Malumphy, et al., 2012)
- Economic Importance: There is no evidence that this scale is established anywhere in the New World, at least on hosts that can survive outside year-round. Florida nurseries are major importers, growers and distributors of many ornamental species that are suitable hosts for this scale. Also, there are many species of native orchids in Florida, some of which are threatened or endangered, that are potentially suitable hosts. Therefore, there is potential for this scale to become a significant economic and ecological pest. (Stocks, 2014a)
- General Remarks: Detailed description and illustration by Ferris (1938a). Photographs in Malumphy, et al., 2012. Ferris (1938) reported this species collected twice (in 1934 and 1935) on orchids in Los Angeles County (Ferris 1938); but it was reported eradicated by Gill (1997).
Illustrations
Citations
- Ali1969a: distribution, host, 41
- Borchs1958a: distribution, 168, 174
- Borchs1963: taxonomy, 1168
- Borchs1966: catalog, distribution, host, taxonomy, 57
- Chambe1925aJC: description, distribution, host, illustration, taxonomy, 85-86
- Chou1982: description, distribution, host, taxonomy, 155, 171-172
- Chou1986: illustration, 573
- DanzigPe1998: catalog, distribution, host, taxonomy, 282-283
- DowellGiJe2016: distribution, 116
- Ferris1938a: description, distribution, host, illustration, taxonomy, SII-143
- Ferris1942: taxonomy, SIV-446:56
- Gill1997: distribution, illustration, taxonomy, 168, 171, 179
- Hua2000: distribution, host, taxonomy, 150
- Hunt1939: distribution, host, 556
- JansenAl2023: dispersal, host, 26
- KondoWa2022a: distribution, host, list, 17
- KozarWa1985: catalog, distribution, 83
- Kozarz1974: host, 23
- Mackie1935: distribution, host, 428
- MalumpHaSa2012: description, host, illustration, life history, taxonomy, 1943.1-1943,11
- MartinLa2011: catalog, distribution, host, 41
- McKenz1956: distribution, host, illustration, taxonomy, 32, 119
- Nakaha1982: distribution, host, 47
- NormarOkMo2019: distribution, phylogeny, 23,59
- PooleGe1997: distribution, 349
- PowellZeMi2024: diagnosis, distribution, host, illustration, key, 3, 5, 8, 19
- Ryan1946: distribution, economic importance, 125
- Ryan1946: distribution, 125
- Stocks2014a: biology, diagnosis, distribution, economic importance, host, illustration, 1-3
- Suh2016: distribution, host, key, 319, 328
- SuhJi2009: distribution, illustration, taxonomy, 1039-1054
- Takagi1970: taxonomy, 13
- Takaha1931b: taxonomy, 380
- Takaha1936a: distribution, host, 220
- Takaha1955e: taxonomy, 70, 71
- Tang1986: distribution, host, illustration, 276
- Tang2001: taxonomy, 3
- Tao1978: distribution, 94
- Tao1999: distribution, host, 82
- VonEll2025: distribution, 38
- Willia2017a: catalog, list of species, 220
- Wu1935: distribution, 239
- Yang1982: distribution, taxonomy, 200, 209